|
GID.info |
|
Gender Identity
Disorder Information |
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Below are the "Top Twenty" questions submitted to the previous version of this site. For a more complete understanding of GID and Intersex disorders you should read all of the content on this site.
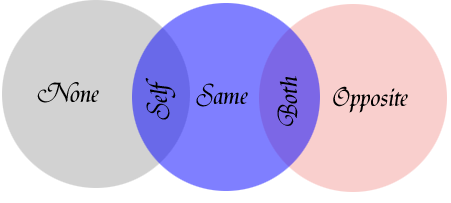
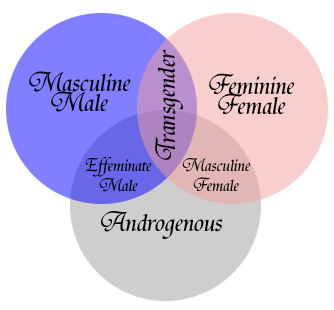
A. In short, it is a disorder that occurs when someone's self-image or identity as one sex is at odds with their physical sex and it causes the person psychological distress called "dysphoria." More detailed information is available on this site in the section titled About GID. Q. What do all these terms like "transgender" MEAN? A. The following list briefly describes the terminology that pertains to people with various forms of Gender Identity Disorders:
GID is a broad clinical classification which may be applied to virtually ANY gender-variant behavior in men or women. Q. Are transgendered people mentally ill or delusional? A. No. Despite the inclusion of Gender Identity Disorders in a catalog of mental illnesses, the American Psychiatric Association (APA) does not consider GID a mental illness (yet they refuse to remove it from the catalog, as they did "homosexuality" in 1973). According the the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Illnesses (DSM-IV-TR), GID meets the criteria for "social non-conformity." Nonetheless, a one-and-only exception to that definition is made, for no apparent reason, to justify the inclusion of GID in the list of Psychosexual Disorders. GID patients are not "delusional" either. Part of the reason for the Standards of Care followed by most doctors is to screen out the patient who presents with apparent GID but may, in fact, be delusional or psychotic. One hallmark is "persistence." Psychotic episodes rarely last for extended periods of time. They are, by nature, "episodic," with periods of normal behavior in between. A person who is truly transgendered will have had a persistent desire to be or belief they are/should be the opposite sex. If a gender patient periodically crossdresses their behavior may APPEAR to be "episodic" to the outside observer, but it is not if the person's GID is present and suppressed during times they do not engage in such activities. Another test is whether or not the psychological distress or perception of the patient responds to psychopharmacology (i.e., "drugs therapy"). True GID does not respond - that is "go away" - with the administration of anti-depressants or anti-psychotic medications. Q. Aren't transgendered people "pedaphiles?" A. By the same (lack of) logic, one could argue "Catholic Priest = Pedaphile." Of course there are some, in as much as there are Police Officers, Firemen, Teachers, Crossing Guards, Ice Cream Vendors, etc. who are pedaphiles. Some transgender people don't even LIKE to be around children, though, as they are constant, if not painful, reminders of their inability to become pregnant and bear them. Q. Are "transgendered" or "intersexed" people gay? A. Not necessarily. Terms like "straight/heterosexual" or "gay/homosexual" can be difficult to apply to people who are physically intersexed or psychologically transgendered. This is because it is a matter of perspective concerning who the "opposite sex" is. Sexual Orientation and Sexual Preference People often argue over whether or not sexual orientation is determined biologically (you are born a certain way) or if it is a "chosen behavior." First off, let's define the terms: Sexual Orientation refers to source of the physical stimulation, fantasies, dreams, etc. that define the total picture of what "turns on" someone. Sexual Preference refers to the actual activities of an individual. In other words, a person may be Bisexually Oriented, but PREFERS only to engage in sexual activity with the opposite sex. SEXUAL ORIENTATION/SEXUAL PREFERENCE
Psychological definitions without physical sex being taken into account: The following are some psychological definitions sometimes used to describe orientation without taking the individual's own sex into account. These are not widely use, probably because they end in "philic/philia" which actually only means "love or fondness," however most people are familiar only with "pedophilia" and wrongly assume ANY word anding in "philic/philia" is a similar criminal perversion. Which is not true!
* There isn't an alteranate psychological term for "bisexual." However, if you follow the Greek roots, "Ambiphelia" - translated as 'love or fondness for both or either' seemed the most appropriate.
As defined by Orientation:
As defined by Preference:
So a people who are male-to-female transsexuals and are attracted to men would be inclined to say, from their perspective, they are "heterosexual." From societies perspective, which places emphasis of sexual identity on physical being, that same person would be considered "homosexual." Q. Isn't being transgendered a "lifestyle choice?" A. The phrase "lifestyle choice" is propoganda and misinformation designed to make people believe that being transgendered (or gay, as there is usually no distinction drawn) "choose" to be as they are. This is because the people who call it a "lifestyle choice" want to believe a person can be talked out of being gay or transgendered. This is patently UNTRUE! Given the social stigma, ostracism, prejudice, and abuse why would ANYONE "choose" to be a social outcast? Why would anyone "choose" to place themselves in a group that is a target of violence? There is a growing body of scientific evidence that people ARE born with a predisposition to their sexual behaviors. While there is no conclusive evidence that there is a biological cause for either homosexuality, recent research strongly suggests there IS a biological cause for transgenderism. Tests performed on animals proved that - once sexual behaiors are set during fetal development - it was not possible to alter the brain structure or behavioral patterns afterward. People should just accept that there is no element of "choice" involved. Many choose to suppress their natural behaviors out of fear, but doing so does not change their self identity and often results in depression and suicide. Q. Aren't "sex" and "gender" the same thing? A. Sex" and "Gender" are not the same thing It is a common misconception that "Sex" and "Gender" are one in the same. For most people these two things are in sync with one another and it seems quite natural - in fact, most people who have no conflicts between their physical sex and their gender identity cannot even understand how such a thing is possible. It, unfortunately, IS possible. "Sex" refers to the physical sexual organs with which a person is born. "Gender" refers to how they perceive themselves psychologically. "Gender" or Psychological Sex
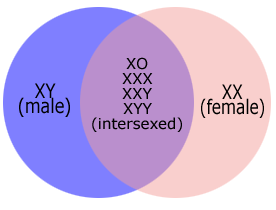
We are usually taught in school that there are only two sexes, MALE and FEMALE. We are also taught that these are defined by our "sex chromosomes," where XX makes a person "female" and XY makes a person "male." What is often overlooked is that there are variations that do not fit into either classification. When this occurs, it is referred to as an "Intersexed Condition." GENETIC SEXES
This occurs far more commonly than is generally known. One estimate (by the Intersex Society of North America) indicates that the total of ALL intersexed conditions is as common as 1 in every 100 births. Because of the wide ranging effects of chromosomal anomolies, however, not all cases of intersexed conditions are identified. The effect on a developing fetus varies widely due to a number of factors. Some of these children are born with what are called "ambiguous genetalia" (the doctor cannot determine if the child is male or female). However, most children born with chromosomal anomolies will appear to physically be either male or female and will be "sexed" as such by the doctor and raised in the assigned gender role. Various physical problems, however, may occur during puberty when contrasexual secondary characteristics may develop (such as breast growth in a "boy" or facial hair on a "girl"). The most common arguement made by the layperson concerning people who have a contrasexual gender identity is that it should be obvious to any fool that "males" have a penis and testicles, and "females" have a vagina and ovaries. As the aforementioned piece on genetics shows, though, this is an over-simplified view of biology. PHYSICAL SEX
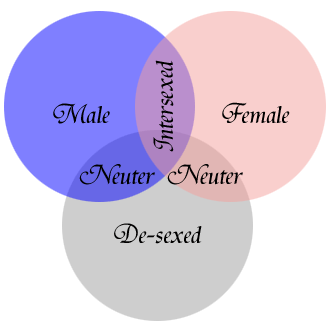
"Males" would, of course, have a penis and testicles. "Females" would have a vagina and ovaries. However, as the piece on genetics shows, there are a number of "Intersexed" conditions where an individual will have characteristics of both sexes (termed "psuedohermaphrodite male" or "psuedohermaphrodite female" because "true hermaphrodites" having two sets of sex organs are exceedingly rare). "Neuter Male" would refer to any male who was hypogonadic (underdeveloped testes) or lacking testes altogether. If the testes were surgically removed it is called a "Bilateral Orchidectomy." Such operations are often performed on men with testicular cancer. "Neuter Female" would refer to any female lacking ovaries. "De-sexed" refers to any person with NO sexual organs of any kind, who may otherwise physically appear to be either male, female, or androgenous. The overlap area of "De-Sexed" and "Intersexed" refers to people without sex organs who's appearance is inconsistent with their apparent sex. Many of these physical sexes are the result of either genetics or surgery. Q. Is there a "cure" for GID? A. In a manner of speaking. Transsexualism, a form of Gender Identity Disorder, is defined by a person who has a sexual self-identification that is at odds with their physcial form. This usually leads to psychological distress called "dysphoria." The aim of treatment for transsexuals is the relief of that distress. In the past many attempts were made to modify the person's thoughts (i.e., mind control or "brain washing"), via hypnosis, aversion therapy, shock therapy, or drug therapy. None of these methods ever proved effective and often did more damage and inflicted more trauma on the patient than anything else. Today the medical community does not advocate any attempts at "changing the patient's mind." Today the focus of medical treatment for transsexualism is on altering the body to more closely conform with the individuals self-image, which may include Sex Reassignment Surgery (SRS) and/or other surgical procedures. It has proved a far easier and much more effective treatment to make a GID patient's body align with their mind than the other way around. More information on such surgical procedures is discussed in the Surgery section of this web site. Q. Does everyone with GID undergo surgery? A. No. As the goal is the relief of psychological distress caused by a person's self-identity being at odds with one's physcial nature, surgery is not always necessary for the individual to find peace of mind. Some people find a "zone of comfort" with their bodies without the need for surgery. For others, surgery may be the only means of relieving their distress and aligning their bodies with their self-image. Q. Why would a guy get his penis chopped off? A. First of all, male-to-female transsexuals and intersexed women who have masculine genitals are NOT "guys!" The answer is no sane MAN would voluntarily have his genitals removed. Transsexuals are not insane, there are safeguards within the Standards of Care that attempt to identify anyone who is. But male-to-female transsexuals and intersexed women are also not "men." Furthermore, in the SRS operation the penis is NOT "chopped off!" The tissue from the penis is used to construct the vagina in the male-to-female transsexual patient. Scrotal tissue is reformed into the labia. The tip of the penis is retained to fashion a clitoris. The only part of the genitals that are actually REMOVED are the testicles. Q. What happens if they want to "turn back?" A. The Standards of Care that is in place has a number of "escape clauses" before anything permenant and irreversible is done for those who are unsure of their gender identities or ability to undergo the process of transition from one gender to the other. This is part of the screening process to make sure only those who are serious and psychologically fit enough complete the process. Very rarely does anyone who makes it all the way through the process of transition decide it was a mistake and revert back to their original gender role. In most of those cases the problem can be traced back to improper candidate screening by a doctor somewhere along the way - especially if the individual had sought transition services outside the Standards of Care guidelines. The International medical community acknowledges SRS as an effective and highly successful treatment for transsexualism. Q. Are "intersexed" or "transsexual" women REAL women? A. Depends on what you mean by "real." There is a group of that call themselves "Womyn Born Womyn" who claim that anyone who was not raised as a girl or had a "female life experience" and cannot bear children is not a "real woman." Thier definition is specifically aimed at exempting Male-to-Female Transsexuals as "women." Many men and women hold similar beliefs, to some extent, by often citing that transsexuals cannot have children. And many of the medical precautions within the Standards of Care are based on the assumption that everyone wishes to have children. This is sometimes called the "Procreation Prejudice." Thier logic, though, is full of holes. First of all, not even every woman is capable of bearing children. An estimated 300 million women on the planet are barren and would not meet the "reproductive requirements" the WBW hold. They also cannot define what being "raised as a girl" or a "female life experience" is. An almost equal number of men throughout the world are similarly incapable of fathering children. Clearly, basing ones claim to "maleness" or "femaleness" on ability to procreate excludes fully 10% of the world's population! And that doesn't include those who CHOOSE not to have children. Take, for example, women who were born with Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome. They are considered "genetically male," and have no ovaries or uterus in much the same way that any woman who has had a hysterectomy doesn't. Yet they are, to any outward examination, female. They are legally female. Born into this world as girls. Raised as girls. And, other than an inability to menstrate, have a "female life experience." A post-operative male-to-female transsexual is essentially in the same physical state as a woman born with AIS. The short answer is that an intersexed or transsexual woman is just as REAL a woman as any. To suggest otherwise is simply ignorant and prejudicial. Q. What is the difference between a Pre-operative Transsexual and a She-Male? A. Physically, nothing, in that both terms refer to a person who was physically male who has been feminized and dresses as a woman, but still has a penis and possibly testicles. The real difference is in "labels." Most "She-Males" are in the "Adult Industry" as prostitutes or porn stars. Some have no desire to actually undergo gender reassignment surgery, but may have surgery, such as implants, to make certain they retain their "manhood" while making the rest of their body look like that of a woman. Many pre-operative transsexuals take offense at being called "She-Males" because of the connotation that they are prostitutes or engage in pornography. Pre-op transsexuals fully intend to live in the opposite gender role from that in which they were reared. Not all of them go through with the gender reassignment surgery (for health reasons, financial reasons, or whatever), but the key difference is that they just want to be "one of the girls." Q. Aren't sex changes "unnatural?" A. Most plants have both male and female sexual organs. Some plants, like various maples, walnuts, and desert shrubs, switch off which parts flower during cross pollination - essentially switching the "sex" of the plant back and forth. The fish species Anthias squamipinnis spontaneously changes from female to male if the number of males is inadequate for propogation. The Blue Head Wrasse fish also has a method of changing females into males through secretion of a sex changing chemical. There is also a species of West African frog (mentioned in the first Jurassic Park movie, by the way) that will spontaneously change sex as well. So it is clear that, in nature, spontaneous sex changes can be part of the natural processes of biology.
Q. Why can't transgendered people realize that men don't wear high heels and dresses? A. Acceptable male or female clothing styles have not been consistent throughout history. Many former signs of a "refined gentleman" or of "noble stature" that commanded respect would be considered "effeminate" today and the wearer despised. For some people with GID problems like "transvestic fetishism," they are sexually aroused by clothing of the opposite sex. But for most people with GID, the clothing is only a means to express themselves. They would prefer to be perceived as the opposite sex and clothing often acts as an overt cue toward achieving that perception. Many of the rigid beliefs about "proper dress" held by Western society today are rooted in Victorian-era beliefs, yet persist. High heel shoes were originally invented for men. The precursor were leather boots with wooden soles designed with "cleats" to hold a Cavalryman's foot in the stirrup while riding at a gallop. What we would call the "modern" high heel shoe became popular for men during the Renaissance period in Europe. It was primarily worn by the "Gentry class" as a way to keep their expensive leather uppers out of the mud and dung that covered the streets and roads of the age. Some women, usually of short stature, also wore high heels. Cathering DiMedeci's "sexy" entry into the French Court in the 1500's literally made history. Because of road and street conditions high heel shoes remained popular as men's wear until the Industrial Revolution of the 1800's - when the "German flat sole shoe" and "Grecian sandal" became popular footwear. The high heel remained for men only on "Cowboy Boots," where it continues to serve the same purpose for which it was originally invented, i.e., keeping a horseman's foot in the stirrup. High heels for women took their cues from Catherine DiMedeci's stunning sashay as a way to exagerate the sway of a woman's hips, elevate her height, and reshape the leg. Men haven't always worn the pants in the family - especially before they were invented. Nobody knows for certain when pants, trousers, etc. were "invented" but it is clear that their popularity as menswear is a relatively recent occurance. Most of the leg coverings worn by men before the modern era were not a single garment. Even our modern words "pants" and "trousers" are plural, referring to the bits of cloth that cover each leg. In most cultures, though, variatious "skirts," "dresses," and "robes" were worn by men. By the mid 1700's men in Europe begin wearing "breeches" (or "britches" informally). These only went from the waist to the knee, where stockings were used to cover the lower leg - because they were easier to clean and less expensive to replace. Stockings could be changed often, while a man might wear the same pair of breeches almost constantly. Pantaloons (from where the word "pants" is derived) did not become popular until the early 1800's. The word, though, first appeared in England in the 1600's to refer to the "clown pants" worn by Italian comedy character "Pantaleone." Around 1800 breeches fell out of favor in continental Europe as well with the French Revolution. Breeches were usually worn by the upper class, while the peasants wore "trousers." The word refers to either drawers, trunks, hose kept in trunks, or to "truss" something. At any rate, they were informal work wear which was looser fit and meant to be rugged and worn all day. Evening wear consisted of Pantaloons, and trousers were often worn over breeches while horseback riding (and also for the upper class to hide their status while on the roads). Sailors had worn a loose fitting "work trouser" since the late 1500's because it was cooler and the legs could be rolled for wading or climbing rigging. What we consider modern pants as a single garment covering from the waist to the ankles, most likely began with the introduction of Khaki pants to the British military in the mid to late 1800's. Cheap knockoffs were manufactured in China called "Chinos" which were sold to other armies, including the United States. Modern blue jeans were invented by Levi Strauss in the American West during this same time period. "Short pants," "Bermuda Shorts," and "Knickerbockers" became popular either where it was hot or for activities like sports or hunting in the early 1900's. "Slacks" were invented in the 1930's by Haggar and referred to a casual trouser to be worn during "slack time" between work and sports. Pants for women started to appear in the form of "Bloomers" in the mid to late 1800's, mostly among women bicyclists and athletes. They were also worn as a form of protest by suffragettes, having much to do with many ordinances making it illegal for a woman to wear anything but a dress or a skirt. Some churches were still refusing entry to women in pants as late as the 1970s! What is deemed "socially acceptable" attire changes with the times and many fashions are "cyclical" and come back into style, in one form or another. Ultimately, though, a persons choice of dress is unlikely to "harm" anyone. After all, it's ONLY clothing Q. How common is GID? A. Part of the problem with estimating the prevalence of GID is that the category is so very broad. There have been no studies aimed at estimating the total number of people who have some form of GID. The best studies have concentrated on diagnosed, post-operative transsexuals. The American Psychiatric Association (APA) publishes the frequency for male-to-female transsexuals who have undergone surgery at 1 in 30,000 and female-to-male at 1 in 100,000. It should be noted, however, that these numbers are based on decades-old data when fewer people were willing to seek treatment for GID and finding a surgeon to perform the SRS operation was more difficult. More recent studies, performed outside the United States, in the late 1980's and 1990's have found a frequency of about 1 in 10,000 for male-to-female transsexuals and 1 in 30,000 for female-to-male transsexuals, which translated to a total frequency of 1 in 2,900 for all transsexuals in one study. These revised numbers, though, STILL only count those who have actually undergone SRS operations. There are many more diagnosed transsexuals who do not seek surgery or have not yet undergone the operation. Psychotherapists who treat GID patients guess that between 1 in 5 to 1 in 10 of all diagnosed transsexuals carry through with surgery. This would mean the TRUE prevalence of all transsexuals is an order of five to ten times greater than that indicated solely by post-operative numbers! These numbers also do not take into account the other kinds of GID such as crossdressers, drag performers, or intersexed people seeking to change gender roles. A more detailed accounting of frequency is available on this site under the section titled prevalence. Q. Why are there more Transgendered MEN than Women? A. Good question, and not one with any clear answer. It might have something to do with women in our society being able to "crossdress" without notice. Nobody pays any attention these days to a woman in a men's tee shirt and jeans, work boots, and most men wouldn't even think it's odd if they saw their girlfriend or wife walking around in men's boxers. Women can also easily wear their hair short or long and engage in a wide variety of "masculine" activities. It may simply be that many "transgender" women are able to satisfy their crossgender needs within the acceptable boundaries of society - and therefore go unnoticed. However, if a man takes to wearing his wife or girlfriend's underwear around the house, or if he steps out into the streets in a skirt and blouse, wears his hair long and styled effeminately, and engages in "feminine" activities it RARELY goes without notice. Since boys are actively discouraged from a very young age from engaging in "feminine" activities, there are very few socially acceptable outlets for a transgender male's crossgender needs. The answer may also lie in biology. The basis for human beings is female. All fetuses start off as female. The determining factor for making a fetus male is the presence of a Y chromosome. The Y chromosome has only a small number of genes on it, compared to the X chromosome. This means that even a minor error in a Y chromosome can have a dramatic effect on the development of the fetus. For girls, however, they have two X chromosomes, each of which has more genes on it than Y chromosomes do. Even if there is an error on one of the X chromosomes, odds are good that the genes are okay on the other X chromosome, so there is little - if any - effect on the development of a female fetus EVEN when there are genetic errors. This is the reason that genetic disorders are far more common in males than females - because males do not have any "backup genes" on another chromosome. IF transgender behaviors are caused by genetic anomolies with the Y chromosome, it may explain why the disorder is more common among men than women. Q. Is GID some kind of "sex fetish?" A. GID is a broad category of gender disorders which DOES include "transvestic fetishism," which is a sexually-motivated crossdressing behavior among heterosexual males, but it is only one of many forms of GID. Most kinds of GID have little, if anything, to do with sexual gratification. A. Nobody is certain. There is ongoing research investigating a biological cause, which assumes that it is a "neurological intersex condition," but there is currently no conclusive evidence of this. Ultimately researchers may have to simply accept that it is just the way some people are and that the cause doesn't really matter. What matters is that society similarly accept that some people just ARE transgendered. There is more information on the biological research in the Medical Research section of this web site. Q. What should I do if I know someone with GID? A. Stand by them! The most important thing you can do is continue to accept the person as your friend or family member! It takes immense bravery to admit something like GID others. Recognize them for trusting you with such personal information. Stand up for them when and where you can. Use gender-appropriate pronouns. They will be facing many social situations where others will be openly hostile toward them. Don't BE one of those people. Whatever their decisions, support them by offering your continued help and affection. Think of what you would do if they had told you they had cancer instead. GID a problem no less deserving of your compassion. Remember that this is a MEDICAL problem, not a MORAL one. Do not judge them! Seek Professional Help! - If your friend or family member is not already seeing therapist, help them to do so. Find a recognized SPECIALIST in "Gender Therapy." Most general mental health care givers are not trained to deal with, nor treat, a problem like GID. If you are having a hard time accepting this yourself, you may also benefit from some kind of counselling. Do not discourage your
friend or family member from exploring their identity. Remember that the
related psychological problems arose from a lifetime of being denied the
opportunity to "be themselves." Different forms of GID respond to
different coping techniques. |