HORMONE
THERAPY: INTRODUCTION
<<
RETURN TO Table of Contents
OBLIGATORY
DISCLAIMER
This
information was compiled by someone who is NOT a doctor and, in fact,
has no medical training at all. It has been collected from multiple
sources and referenced as to source whenever possible. Some sources
are reputable medical authorities, others are questionable. The author
of this HRT information makes no value judgements on the sources or
their validity. However, the author does have personal experience with
hormone therapy under physicians' supervision. It is strongly recommended
that you do not use this information for the purposes of self-medicating
with hormones as this can be dangerous - even deadly! Never take any
prescription medications without consulting a doctor. This is for informational
purposes only and this web site and its creator are not responsible
for misuse or abuse of this information or any injury or harm that may
result.
GENERAL
INFORMATION
There
is a lot of research being done on the effectiveness of HRT drugs. Unfortunately
most of the recent studies that have made news headlines are referring
to hormone therapy for post-menopausal women, and in many cases the
sample groups were quite small. What implications, if any, these studies
may have to HRT for transsexual or intersexed people remains unknown.
Also, these studies looked exclusively at the synthetic HRT drugs and
the data conclusions may not apply to bio-identical hormones at all
(and likely do not).
Methods
of Delivery/Administration
(in descending
order of approximate efficiency in delivery into bloodstream)
Intramuscular
injection - 100% efficient
Transdermal (patch, gel, or cream) - 90%
Sublingual troche [under tongue] or nasal
spray - 80%
Oral - 10%
Understanding
"Enteric Coatings"
There isn't just
one enteric coating that is used industry-wide. There are many different
formulations that are used for different applications (i.e., one for
gelcaps, one for granules, another for tablets, etc.). Here's a link
to one company that makes the coatings for pharmaceutical companies:
www.idealcures.com/enteric-coating.html
(where it says "weight gain" in their table, don't worry,
they're talking about how much weight it adds to the pills coated
with it). The entire purpose of these coatings is to allow them to
survive through stomach acids - saliva isn't going to dissolve the
coating, so for those who've planned to dissolve such pills under
your tongue (sublingual administration), enteric coated pills won't
work for that. You'd have to "breach the barrier" to absorb
the medication sublingually (i.e., puncture the gelcap or crush the
tablet). SOME will invariably go down your throat and into your stomach
- and these coatings are usually added for a limited number of reasons.
Either:
- because the
medication is likely to make your stomach upset if dissolved there.
- to time-release
the medication instead of all at once.
- to target the
medication to the small intestine.
Coated meds are
usually labeled as being "Enteric Coated" or "Time
Release" or "Targeted Medication" (or words to that
effect). Some people are allergic to the coatings themselves and labeling
regulations require the packaging indicate such coatings are present.
In
addition to those studies, other research into the biochemical effects
of HRT medications at the genetic level are also underway. This page
will be updated with information as it becomes available.
The
"Hormone Chain" Explained
One
thing that is very difficult for people to understand is how the human
body produces hormones. Before anyone considers purposely altering
their hormone balance I feel it is important to know the way it's
all supposed to work.
Steroids
of the Adrenal Cortex
The adrenal cortex
is responsible for production of three major classes of steroid hormones:
- glucocorticoids,
which regulate carbohydrate metabolism;
- mineralocorticoids,
which regulate the body levels of sodium and potassium; and
- androgens,
whose actions are similar to that of steroids produced by the male
gonads.
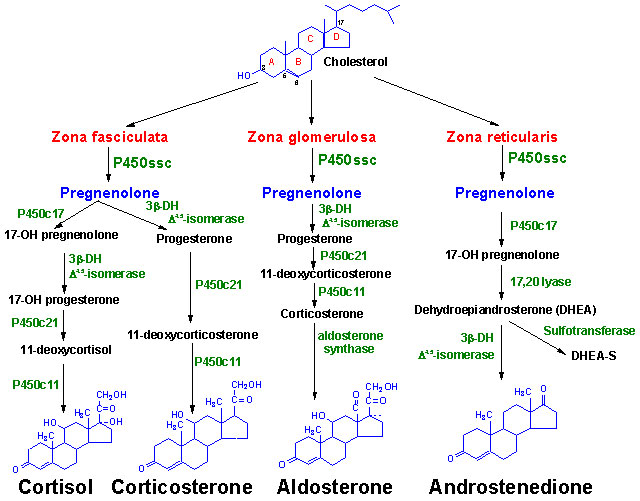
The adrenal cortex
is composed of three main tissue regions: zona glomerulosa,
zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis. Although
the pathway to pregnenolone synthesis is the same in all
zones of the cortex, the structure of the tissues and enzymes present
in each zone are distinct, with the exact steroid hormone product
dependent on the enzymes present in the cells of each zone. Think
of them like three factories all receiving the same raw materials
but cranking out different product lines.
Gonadal
Steroid Hormones
Although many
steroids are produced by the testes and the ovaries, the two most
important are testosterone and estradiol. These
hormones are under tight control with short and long negative feedback
loops to the brain regulating the secretion of follicle stimulating
hormone (FSH) and leutinizing hormone (LH) by the pituitary
gland and gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
Low levels of
circulating sex hormone in the blood reduce feedback inhibition on
GnRH (the long loop), leading to elevated FSH and
LH. The pathway to sex hormones in both male and female gonadal
tissue (i.e, sex organs) includes the production of androgens: androstenedione
and dehydroepiandrosterone. Testes and ovaries contain an
additional enzyme, a 17b-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, that
enables androgens to be converted into testosterone.
IN MALES:
LH binds to Leydig cells (in the testes),
stimulating production of the principal Leydig cell hormone,
testosterone. Testosterone is secreted to the blood
and also carried to Sertoli cells (elsewhere in the testes)
by androgen binding protein (ABP). In Sertoli cells
the testosterone is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Testosterone and DHT are carried in the bloodstream
to target tissues by a specific gonadal-steroid binding globulin
(GBG)*. In a number of target tissues, the testosterone
can be converted to DHT "on site." DHT
is the most potent of the male steroid hormones, with an activity
that is 10 times that of testosterone. Because
of its relatively lower potency, testosterone is sometimes
actually considered to be a "prohormone" (another name for
a "hormone precursor").
Testosterone
is also produced by Sertoli cells but in these cells it is
regulated by FSH. FSH stimulates Sertoli cells
to secrete androgen-binding protein (ABP), which transports
testosterone and DHT from Leydig cells
to the place in the testes where sperm are made, where the testosterone
stimulates sperm production.
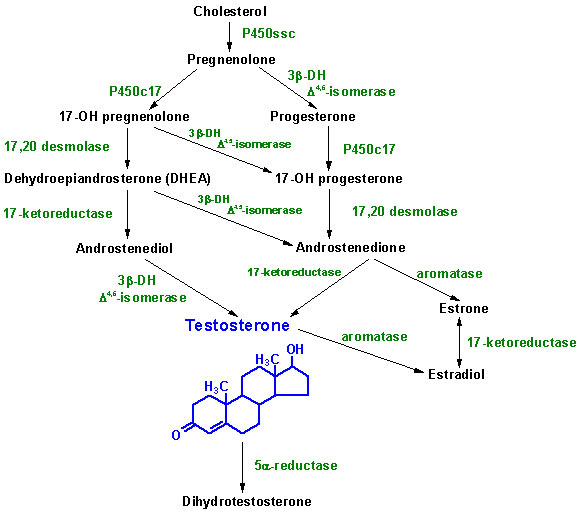
IN
FEMALES: LH
binds to Thecal cells in the ovaries, where it stimulates
the production of androstenedione and testosterone.
An additional enzyme known as aromatase is responsible for
the final conversion of androstenedione and testosterone
into the estrogens.
Aromatase
activity is also found in Granulosa cells, but in these cells
the activity is stimulated by FSH. Normally, Thecal cell
androgens produced in response to LH diffuse to Granulosa
cells, where Granulosa cell aromatase converts these
androgens to estrogens.
As
Granulosa cells mature they develop large numbers of LH
receptors becoming increasingly responsive to the presence of
LH, increasing the quantity of estrogen produced
from these cells. Granulosa cell estrogens are largely, if
not all, secreted into follicular fluid. Thecal cell estrogens
are secreted largely into the bloodstream, where they are delivered
to target tissue by the same globulin (GBG)* used to transport testosterone.
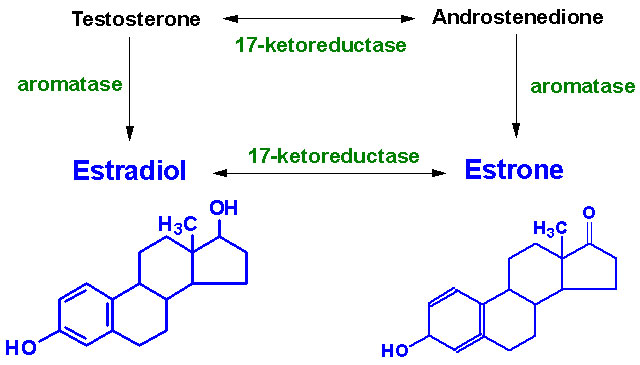
IN
BOTH MALES & FEMALES:
Aromatase is found in numerous tissues in both males and females,
being especially prevelant in adipose (fatty) tissue, but also in
muscular tissues. There it converts testosterone and androstenedione
into estrogens. In males the conversion in adipose tissues are the
principle source of estrogens.
5-alpha-Reductase
(5-AR) is responsible in both males and females for the enzymatic
conversion of Testosterone to DHT and Progesterone
to Dihydroprogesterone (DHP). 5-AR occurs throughout the
body but occurs in to forms. Type I (5-R1) is the primary
form active in acne and sebaceous gland oil secretions in the skin
but is most abundant in the liver where it catabolizes steroids. Type
II (5-R2) is primarily expressed in target tissues for androgens,
such as the prostate and seminal vesicles, though it has been found
present in the oil around hair follicles as well.
*Another
name for that globulin is "Sex Hormone Binding Globulin"
(SHBG).
This
info lifted from the
Indiana State University Medical Biochemistry web site.
WARNINGS
FOR EVERYONE
The
important thing to keep in mind is that hormone therapies are tailored
to the individual's body chemistry. A proper dosage for one person may
not be the proper dosage for another person. That is why it is imparitive
to have a doctor monitoring you and doing regular blood work.
Hormones
are nothing to be taken lightly. They can potentially KILL
you if they are misused!
BLOOD
CLOTS
Here's some information
about the risk factor (this is in relation to post-menopausal women,
by the way, but I think it might be reasonable to assume that men
might have at least a similar risk, if not more-so since cardiovascular
problems are much more prevelant among the male population).
NEW YORK,
March 14, 2000 (Reuters) -- Women who take estrogen after menopause
have a greater risk of developing blood clots in the legs or lungs
in the first year of hormone use, a new study suggests. The association
holds true whether a woman takes estrogen by pill or patch, alone
or in combination with other hormones, or in high or low doses.
However, the risk drops sharply after the one-year mark.
After that, a hormone-user appears to be at no greater risk of blood
clots than other women, according to the report in the March 15
issue of the British Medical Journal.
Overall,
a woman has a 1.3 in 10,000 risk of developing such clots,
which can be life-threatening if they lodge in the lungs. A woman's
risk of clots rises to roughly 3 to 4 in 10,000 if she is taking
estrogen, reported researchers from Madrid and Barcelona, Spain.
When used for extended periods, estrogen replacement therapy (ERT)
is thought to greatly lower the risk of heart disease and the bone-thinning
disorder, osteoporosis. In the short term, ERT can help reduce menopausal
symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats.
While estrogen
does increase the risk of uterine cancer, most women also take progestin,
a hormone that helps to reduce that risk. The new study included
292 women, aged 50 to 79, who were diagnosed with lung or leg clots.
The researchers compared the women to 10,000 other randomly selected
women the same age. Overall, women have four to five times greater
risk of developing a clot in the first 6 months of taking hormones,
and a three times greater risk at 6 to 12 months of taking estrogen.
Other risk factors for such clots include a history of varicose
veins, removal of both ovaries, obesity, and smoking. A leg clot,
or deep vein thrombosis, is characterized by pain, swelling and
warmth, and discoloration of the skin on the affected leg. A lung
clot can cause shortness of breath, chest pain and fever.
What can you do
to prevent the possibility of blood clots? Well, don't smoke, make
sure to excercise regularly, and eat right. If there is a history
of coronary problems in your family, you're most likely a contender
for cardiovascular problems as well and should take that into consideration.
A couple aspirin a day is supposed to be healthy and prevent clotting
because it acts as a blood thinner, but NEVER
start an aspirin therapy without consulting a physician first!
LIVER
DAMAGE
The liver is the
largest organ inside your body and it performs over 500 functions
and is the primary "detox" center of your body, seperating
the good stuff from the bad stuff and then passing on the good stuff
to the rest of the body while sending the bad stuff to the gall bladder
and kidneys for further processing and disposal (that is a VERY simplistic
version of the process, by the way). And that literally means EVERYTHING
that winds up in your blood or stomach - alcohol, pesticides on foods
you eat, chemicals absorbed through your skin, fumes inhaled, etc.
We live in a VERY toxic world, and your liver is putting in a lot
of Over Time just trying to deal with it. Even things we normally
don't think of as "toxic" can be if the liver is overworked
or malfunctioning. A high protein diet can, for example, lead to unwanted
Amonia in your bloodstream (it is a byproduct of metabolizing proteins).
Too much amonia in the blood can lead to dementia, among other things.
Okay, now that the scare is on and you're ready to live in a bubble,
you should also know that the liver can do it's job even when 80%
of it's tissues are damaged. That doesn't mean you shouldn't care
what you do to it, though.
As part of its
"detox duties" it also has to deal with a number of hormones.
For example, it is supposed to clear out extra insulin. If it doesn't,
the insulin remains in circulation and continues to do its job of
lowering blood sugar. Failure to dispose of adrenaline (the "fight"
or"flight" hormone) after it has outlived its usefulness may lead
to chronic irritability and temper explosions.
All products absorbed
through digestion initially pass through the liver. THIS is why ingested
hormones CAN POTENTIALLY damage the liver. The liver is supposed to
take care of "excess" hormone production. Ideally, if you
are trying to infuse your system with hormones, you want them to make
a complete circuit through your body, bonding to receptors along the
way, BEFORE the blood gets to the liver. Otherwise there are just
too many hormones for the liver to deal with. But it is also important
to consider WHICH hormones actually do damage. It is well-documented
that synthetic anabolic steroids or testosterone derivitives damage
the liver. I had difficulty understanding exactly HOW they damage
it, but I gathered that the enzymes employed in breaking down the
"natural" hormones into harmless compounds often "accidently"
break synthetics down into toxic substances that cause cellular-level
damage. But what abodut estrogen? In some cases, even as little as
two or three weeks of use have been documented to ruin the ability
of the liver to detoxify natural estrogen. The livers of women
on B vitamin/protein deficient diets may have difficulty metabolizing
estrogen to non-toxic estriol, leaving it instead in the form of liver
toxic estradiol. Estradiol is the form associated with hyper emotional
states including explosive temper and obsessive-compulsive tendencies
(essentially, PMS).
The main problem
with taking hormones orally is that the hormones are passed into the
liver as part of the process of digestion. Not only will some of the
hormones be destroyed in the process, the liver is designed to deal
with small amounts of "left overs" and will be inundated
by the large amount of hormones - some of which will likely be liver-toxic
and cause cellular damage to the organ. Whatever the liver can't handle
will ultimately be washed out the "downstream" side of the
liver into the cardiovascular circuit where the hormones will be pushed
all around the body, binding to receptors as they go, before the blood
returns to the liver. The problem with this scenario is that it is
the REVERSE of the process for hormones produced within the
body.
So, obviously,
if you are going to have estrogen passing through your liver BEFORE
it gets into the rest of your bloodstream, you'd avoid liver-toxic
(i.e., liver damaging) effects if the hormones were "ESTRIOL"
in form instead of "ESTRADIOL." Estriol is available and
is also the main component of a supplement knowns as "Tri-Est"
(Triple Estrogen) which is 80% Estriol, 10% Estradiol, and 10% Estrone.
M2F Transsexuals report unsatisfactory feminization from estriol,
as it is a relatively weak cell stimulator (i.e., it doesn't stimulate
the growth of breast tissue as much as estradiol or estrone).
So how much is
too much? That's unknown and would vary person to person and also
depend on the concentrations of consumed. One thing you can do to
mitigate this problem is to take estradiol transdermally (patch, lotion,
or gel), sublingually (under the tongue), nasally (there is a spray
available), or by intramuscular injection. All of those methods allow
the hormone to enter the bloodstream first which means there is better
efficiency and only waste product hormones will go through the liver
in much smaller amounts.
I have had great
difficulty in determining exactly how damaging elevated estradiol
levels may be to one's liver. A recent study published in Oncology:
International Journal of Cancer Research and Treatment a hospital-based
case controlled study of male liver cancer patients in Greece looked
specifically at the phenomena of elevated estradiol levels in such
patients. It looked at 98 cancer patients and 111 control cases. It
had been claimed that the elevated estradiol levels may have been
responsible for the liver damage, however that claim was not supported
by this study. When the researchers compensated for the fact the cancer
patients' livers were compromised, and therefore incapable of dealing
with steroid hormones efficiently, the conclusion was that the elevated
estradiol levels were a consequence of the liver damage, not the cause
of it. [
source ]
Part of the difficulty
in determining what the actual liver damage risk is posed by estradiol
is that there are too many variables to simply say you have X% chance
of harming your liver if you take oral estradiol. If your liver is
already compromised by pre-existing liver disease, or you have a predisposition
to liver-related complications, or if you mega-dose (as mentioned
above) thus consuming "toxic" levels, you're obviously going
to have a far greater risk than someone without such factors.
See the section
on Progesterone below for liver toxicity information regarding
that hormone.
MOOD
SWINGS & DEPRESSION
Hormones also
alter your brain chemistry. This can lead to wild mood swings, uncontrollable
emotional outbursts, and in some people HRT can cause severe depression
or suicidal tendencies. If you are taking HRT medications and experience
any of these side-effects you should discuss them with your physician
as they indicate a negative reaction to the drugs. There may be alternatives
you could take that would be better tolerated. MANY gender patients
commit suicide and some of those deaths may have been attributable
to HRT medications.
USE
OF HRT DRUGS WITH ANTI-DEPRESSANTS/ANTI-ANXIETY MEDICATIONS
It
is extremely common for gender patients to be concurrently using an
anti-depressant medication with their HRT drugs. What doctors are
NOT telling their patients, and is (to the best of my knowledge) generally
not stated in the prescribing or patient information for the drugs,
is the possible negative interactions between anti-depressant and
hormone replacement therapy medications.
ESTROGEN
- acts upon neurotransmitters in the same way as MAOI anti-depressants
by increasing 5-HT-2 serotonin receptor binding as well as activating
additional serotonin receptors and the overall concentration of serotonin.
It also increases norepinephrine binding to receptors and the turnover
(breakdown and replacement) rate for norepinephrine.
PROGESTERONE
- acts upon neurotransmitters in a similar manner to SSRI
anti-depressants. It inhibits re-uptake of serotonin by receptors
and also inhibits the breakdown of the neurotransmitter thus increasing
concentrations of it. Progesterone also increases the serum levels
of norepinephrine but inhibits binding of it to receptors. Synthetic
progestins appear to have a similar chemical action on neurotransmitters
and have been directly linked to HRT-associated depression.
As
a quick primer on these neurotransmitters:
Serotonin
- low levels of activity (absorbtion) are associated with depression,
high levels of activity are association with anxiety disorders. SSRI's
increase the amount of serotonin by inhibiting how much the body can
act on the body via receptors. For those with a naturally low amount
the increase in intracellular concentration can alleviate depression.
For those with a naturally high amount the inhibition of the receptors
prevents some of the concentrated amount from acting on the body,
reducing anxiety.
Norephinephrine
- one of the metabolites of dopamine, this chemical is part of the
body's system for responding to stress. Low levels of norepinephrine
are associated with sluggishness, mental stress, and depression while
high levels increase heart-rate, respiration, and increase energy
levels (sometimes leading to nervousness or anxiety).
Serotonin
and Norepinephrine levels are apparently linked and, in a healthy
individual, are kept in balance to prevent episodes of depression
or anxiety. The fluctuations in hormone levels experienced by women
during their cycle (and the drop in hormones at menopause) adversely
affect BOTH of these neurotransmitters, leading to mood disorders.
SSRI and MAOI drugs prescribed to treat depression and anxiety problems
also affect BOTH serotonin and norepinephrine levels.
Few transgendered
people seem to be aware of the MAOI and SSRI effects of estrogen and
progesterone, nor are they aware of potential adverse interactions
between their HRT and anti-depressant/anti-anxiety medications. If
you were taking an MAOI or SSRI for depression or anxiety before beginning
HRT you may need to adjust your dosage once you are taking hormones
(I'm inclined to say you'll probably have to reduce it, but you should
talk to your doctor first). If, after you've been on HRT for a while,
you are experiencing anxiety or depression an adjustement to your
HRT regimen may be in order, and as a last resort the addition of
an MAOI or SSRI.
Depression and
anxiety disorders plague the majority of transgendered people, for
which many are taking either SSRIs or MAOIs. Evidence suggests that
the suicide rate alone among trangendered people is a whopping 50
percent* (* see update info Morbidity & Mortality) and the author of this site has to now wonder how many of
those suicides were chemically induced because patients (or even their
doctors) were unaware of the action hormone therapy has on serotonin
and norepinephrine. Since estrogen, progesterone, SSRIs, and MAOIs
do not appear to be listed as counterindications in patient and prescribing
information, even though they act on the same neurotransmitters, seems
a horrible oversight.
PERMENANT
STERILITY & SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION
For biological
males taking female hormones there is a risk of permenant sterility.
This can happen rather quickly (some reports say in as little as three
weeks), but is generally considered irreversible after six months
of hormone use. This effect may be reversible before that timeframe
however, and some are capable of reviving fertility even after the
six month mark. Individual reaction to hormones, which medications
are used, and quantity will all be factors. The author of this site
strongly recommends that those who are concerned about losing fertility
and/or sexual function reconsider medicating with hormones altogether.
If your plans include having a child of your own, M2Fs should consider
banking sperm and F2Ms storing eggs before beginning a counter-sexual
hormone therapy. F2Ms and M2Fs will also need to consider that post-operatively
they will not have a womb and any use of the stored eggs or banked
sperm would require a surrogate (if you're lucky that might be your
girlfriend or wife).
<<
RETURN TO Table of Contents
|



